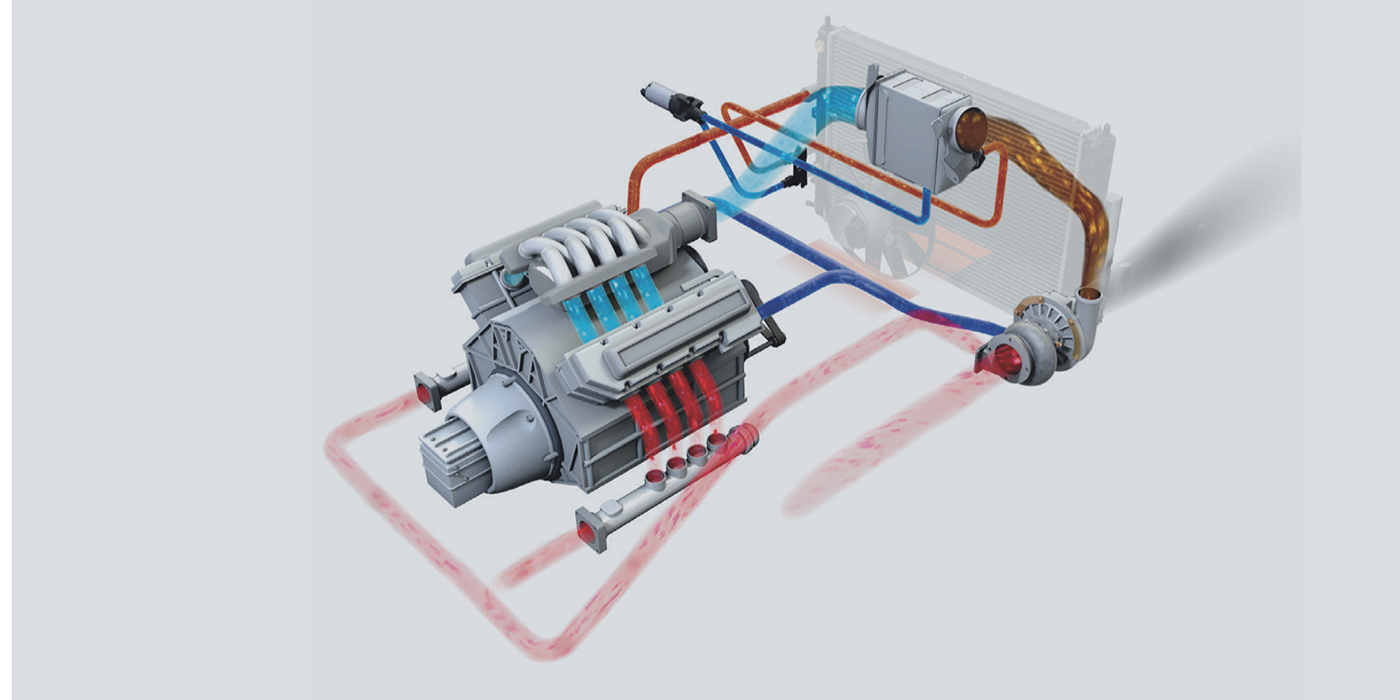
Modern engines are far more sophisticated than ever before, designed to deliver higher performance while meeting increasingly strict environmental and efficiency standards. As expectations continue to rise, the role of thermal management has become a central part of ensuring reliability, extending component lifespan, and maintaining optimal engine performance. Businesses operating within automotive, transport, and heavy-machinery sectors are beginning to recognise that strategic thermal control is not just a technical requirement—it is a competitive advantage.
The Critical Importance of Temperature Regulation
Temperature regulation influences nearly every aspect of engine behaviour. Whether an engine is powering a light commercial vehicle or a high-output industrial machine, heat generated during combustion and friction must be controlled. Excess heat leads to metal fatigue, lubricant degradation, and excessive emissions, while insufficient heat can result in reduced efficiency and incomplete combustion. Striking the right balance is crucial, and this is where advanced thermal systems step in to maintain stability under a wide range of operating conditions.
In recent years, engineering teams have invested heavily in more intelligent thermal solutions. These include multi-coolant routing systems, integrated heat exchangers, and active monitoring using onboard diagnostics. The goal is simple: to keep engines performing consistently, even under demanding loads. As manufacturing standards evolve, thermal management continues to shift from a reactive measure to a proactive design principle.
Improving Efficiency Through Component Integration
One of the biggest transformations in engine technology is the move toward integrating thermal management directly into the engine’s structural and functional components. Heat exchangers, sensors, pumps, and thermostatic controls now work together rather than in isolation. When systems communicate with each other, engines adapt more quickly to external conditions, enabling better fuel efficiency and reduced wear.
For example, components designed to handle exhaust gases must operate within precise temperature zones to maintain emissions compliance. This is where supporting parts such as the egr cooler contribute to stable temperature control by ensuring recycled exhaust gas enters the combustion chamber at a manageable level. Mentioning this highlights how even a single component can play a major role in broader engine efficiency and environmental strategy.
Extending Engine Life and Reducing Maintenance Costs
Businesses are increasingly aware of the cost implications of poor thermal regulation. Overheating can cause cracking, gasket failure, turbocharger fatigue, and a long list of preventable issues that lead to downtime and significant repair expenses. In a commercial environment where reliability is essential, these disruptions are more than inconvenient—they can directly impact profit margins, logistics timelines, and client relationships.
A well-designed thermal management system helps reduce the long-term stress placed on engine materials. This improves operational stability, maximises performance consistency, and ultimately reduces the frequency of major repairs. Companies that invest in enhanced cooling pathways, improved airflow systems, and robust thermal coatings often find that the upfront cost is offset by long-term savings and improved asset lifespan.
Sustainability Through Smarter Thermal Engineering
Environmental responsibility continues to shape modern engineering decisions. Thermal efficiency directly influences emissions, fuel consumption, and compliance with regulatory frameworks. As governments expand emissions legislation, industries must prioritise sustainable engine design to avoid penalties and stay competitive.
Smarter thermal engineering supports cleaner combustion by stabilising temperatures and improving system responsiveness. With reliable heat control, engines operate closer to their optimal range, reducing pollutants and lowering overall environmental impact. This aligns with global sustainability goals and helps brands build trust with environmentally conscious customers.
Industry Trends and Future Developments
Emerging technologies are reshaping the future of engine thermal management. Electric coolant pumps, real-time heat mapping sensors, and advanced heat-resistant materials are already being incorporated into next-generation engines. In addition, hybrid systems benefit from dual thermal approaches that manage both traditional combustion heat and the unique thermal demands of battery-electric components.
Current news suggests that the automotive industry is accelerating research into improved cooling solutions as part of its transition toward cleaner, more efficient engines. Recent reports highlight how manufacturers are integrating AI-driven predictive diagnostics to detect heat-related risks earlier than ever before. These developments mark a major shift toward preventative design and long-term sustainability.